Clinical Practice Guideline For The Penaksiran And Management Of

Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of acute.
Clinical Practice Guideline For The Penaksiran And Management
This guideline sets out an antimicrobial prescribing strategy for acute sinusitis. it aims to limit antibiotic use and reduce antimicrobial resistance. acute sinusitis is usually caused by a virus, lasts for about 2 to 3 weeks, and most people get better without antibiotics. withholding antibiotics rarely leads to complications. See full list on academic. oup. com. An executive summary of the original adult sinusitis guideline 1 was first sent to a panel of expert reviewers who were asked to assess the key action statements and decide if they should be revised, be kept as stands, or removed based on relevancy, omissions, or controversies that the guideline spurred and to identify any new literature or treatments that might affect the guideline. This guideline addresses several issues in the management of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis (abrs), including (1) inability of existing clinical criteria to accurately differentiate bacterial from viral acute rhinosinusitis, leading to excessive and inappropriate antimicrobial therapy; (2) gaps in knowledge and quality evidence regarding empiric antimicrobial therapy for abrs due to imprecise patient selection criteria; (tiga) changing prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of bact
Rhinosinusitis Infectious Diseases Society Of America
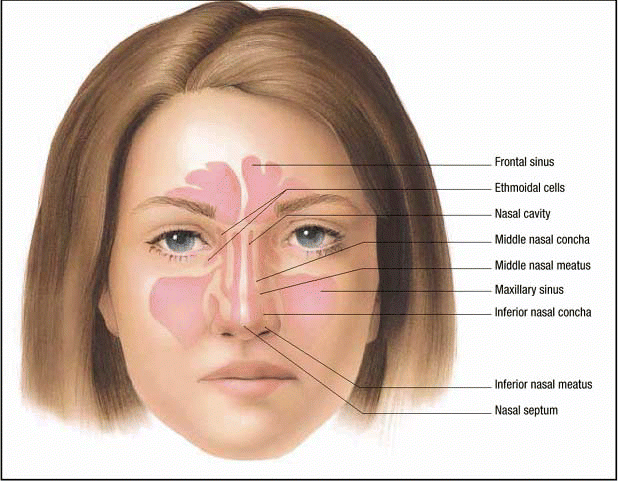
Throughout this guideline, the term rhinosinusitis is used interchangeably with sinusitis. because the nasal mucosa is contiguous with that of the paranasal sinuses, any inflammation of the sinuses is almost always accompanied by inflammation of the nasal cavity [7, 8]. rhinosinusitis is an extremely common condition. Dermatitis/eczema, allergic conjunctivitis, chronic sinusitis and chronic otitis media with effusion. it is therefore timely to develop this first national guideline which incorporates the best available evidence from the scientific literature and expert consensus, to assist primary care physicians in the management of rhinosinusitis. i hope. Term rhinosinusitis is preferred because sinusitis is almost always accompanied by inflammation of the contiguous nasal mucosa. 11-13 therefore, rhinosinus-itis is used in the remainder of the guideline. • uncomplicated rhinosinusitis is defined as rhino-sinusitis without clinically evident extension of. 1 apr 2012 evidence-based guidelines for the penaksiran and initial management of suspected acute bacterial rhinosinusitis in adults and children were .
American academy of otolaryngology (aao) clinical practice guideline (update): adult sinusitis (rosenfeld, 2015), and the american guideline sinusitis academy of pediatrics (aap) clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of acute bacterial sinusitis in children aged 1 to 18 years (wald, 2013) recommend considering watchful waiting using shared decision-making. Pediatric acute bacterial sinusitis (abs) guideline laman dua 19. feb15doh. final. title: microsoft powerpoint final. pediatric acute bacterial sinusitis (abs). pptx.
Penaksiran And Management Of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis Aap Org

Abstract objective: this update of a 2007 guideline from the american academy of otolaryngology--head and neck surgery foundation provides evidence-based recommendations to manage adult rhinosinusitis, defined as symptomatic inflammation of the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity. In reference to other guidelines, infectious diseases society of america (idsa) clinical practice guideline for acute bacterial rhinosinusitis in children and adults .
Throughout this guideline, the term rhinosinusitis is used interchangeably with sinusitis. because the nasal mucosa is contiguous with that of the paranasal sinuses, any inflammation of the sinuses is almost always accompanied by inflammation of the nasal cavity [7, 8]. rhinosinusitis is an extremely common condition. in a national health informasi lapangan conducted during 2008, nearly 1 in 7 (13. 4%) of all noninstitutionalized adults aged ≥18 years were diagnosed with rhinosinusitis within the previous Evidence-based management scheme for adults with chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps for primary care and non-ent specialists. 13. Pediatric acute bacterial sinusitis (abs) guideline page dua 19. feb15doh. final. title: microsoft powerpoint final. pediatric acute bacterial sinusitis (abs). pptx. 2013 aap guideline. ellen r. wald sinusitis (abs) when a child with an upper respiratory infection (uri) acute sinusitis “persistent symptoms”. ▫ 10–30 .
Adult sinusitis (affirmation of value, april 2020) the guideline, adult sinusitis, was developed by the american academy of oyolaryngology-head and neck surgery and was reviewed and categorized as. Treatment guidelines available for penaksiran and management of acute sinusitis in india. tiga. need for a stg/ guideline purpose. there is widespread . The guideline was published as a supplement in the april 2015 issue of otolaryngology—head and neck surgery. the purpose of this multidisciplinary guideline is to identify quality improvement opportunities in managing adult rhinosinusitis and to create explicit and actionable recommendations to implement guideline sinusitis these opportunities in clinical practice. The guideline was published as a supplement in the april 2015 issue of otolaryngology—head and neck surgery.. the purpose of this multidisciplinary guideline is to identify quality improvement opportunities in managing adult rhinosinusitis and to create explicit and actionable recommendations to implement these opportunities in clinical practice.
Access the aafp clinical practice guideline on adult sinusitis. acute bacterial rhinosinusitis (abrs) should be distinguished from acute rhinosinusitis due to . 1. the following clinical presentations (any of 3) are recommended for identifying patients with acute bacterial vs viral rhinosinusitis: 1. i. onset with persistent symptoms or signs compatible with acute rhinosinusitis, lasting for ≥10 days without any evidence of clinical improvement (strong, low-moderate); dua. ii. onset with severe symptoms or signs of high fever (≥39°c [102°f]) and purulent nasal discharge or facial pain lasting for at least tiga–4 consecutive days at the beginning of illnes
24 jun 2013 version of the guideline (2001). results: the diagnosis of acute bacterial sinusitis is made when a child with an acute upper respiratory tract . American academy of otolaryngology (aao) clinical practice guideline (update): adult sinusitis (rosenfeld, 2015), and the american academy of pediatrics (aap) clinical practice guideline for the penaksiran and management of acute bacterial sinusitis in children aged 1 to 18 years (wald, guideline sinusitis 2013) recommend considering watchful waiting using shared decision-making. Acute bacterial sinusitis is a common complication of viral upper respiratory infection (uri) or allergic inflammation. using stringent criteria to define acute sinusitis, it has been observed that between 6% and 7% of children seeking care for respiratory symptoms has an illness consistent with this definition. 1–4.
Posting Komentar untuk "Guideline Sinusitis"